I. Introduction to Blender Sculpting
A. Understanding the Basics of Sculpting in Blender
Sculpting in Blender involves the creation and manipulation of 3D models through digital sculpting tools. Whether it’s refining intricate details or adding depth to organic shapes, Blender’s sculpting feature enables artists to craft visually captivating models with precision and artistry. Utilizing sculpting brushes and the sculpting workspace, artists can unleash their creativity and bring their artistic vision to life.
B. Importance of Sculpting in 3D Design
Sculpting is indispensable in the realm of 3D design, particularly in creating lifelike characters, creatures, and organic structures. It is extensively employed in various industries such as gaming, animation, film, and product design. The ability to sculpt detailed and expressive models adds depth and realism to 3D designs, making it an invaluable skill for 3D artists and designers alike.

II. Getting Started with Sculpt Mode
A. Activating and Accessing Sculpt Mode in Blender
To delve into the world of digital sculpting in Blender, users must navigate to the sculpting workspace, which provides a dedicated environment for sculpting tasks. The sculpt mode unlocks a suite of sculpting tools and brushes, offering a seamless transition from traditional modeling to more organic and artistic forms.
B. Navigating the User Interface for Sculpting
Navigating the sculpting workspace entails understanding the layout, panels, and brush settings that play a pivotal role in sculpting. Familiarity with viewport navigation, camera controls, and tool presets allows artists to navigate the sculpting interface with ease, enabling them to focus on their creative process.
III. Essential Sculpting Tools and Brushes
A. Exploring Fundamental Sculpting Tools
Basic sculpting tools like Grab, Draw, and Smooth form the backbone of sculpting in Blender. These tools enable artists to shape, manipulate, and refine the surfaces of their 3D models. Their versatility and precision make them essential for sculpting projects of varying complexity.
B. Mastering Advanced Sculpting Brushes
Advanced sculpting brushes, such as Clay Strips, Crease, and Flatten, offer a broader range of sculpting capabilities. Adept use of these brushes allows artists to add intricate details, create surface textures, and define the shape and form of their models with enhanced control.

IV. Sculpting Techniques and Workflows
A. Understanding Blocking and Refining Processes
The sculpting workflow typically begins with blocking the primary shapes and forms of the model. Subsequently, artists progress to refining, during which they add intricate details, contours, and textures to achieve a polished and realistic appearance.
B. Employing Dynamic Topology for Adaptive Mesh Detailing
Dynamic Topology allows artists to adaptively adjust mesh density based on the level of detail required. This feature empowers artists to focus on specific areas of their models without being constrained by pre-defined mesh density.
V. Creating Organic Forms and Character Sculpting
A. Sculpting Organic Shapes and Structures
Sculpting organic elements, such as flora, fauna, or natural landscapes, involves understanding and replicating the nuanced details found in the natural world. This process demands a keen eye for natural forms, textures, and a deep understanding of organic structure.
B. Character Sculpting and Facial Features
Character sculpting entails capturing the essence of human anatomy, expressions, and intricate facial features. Achieving lifelike character sculpting requires a deep understanding of human proportions, facial anatomy, and the ability to convey emotional expression through the sculpted model.
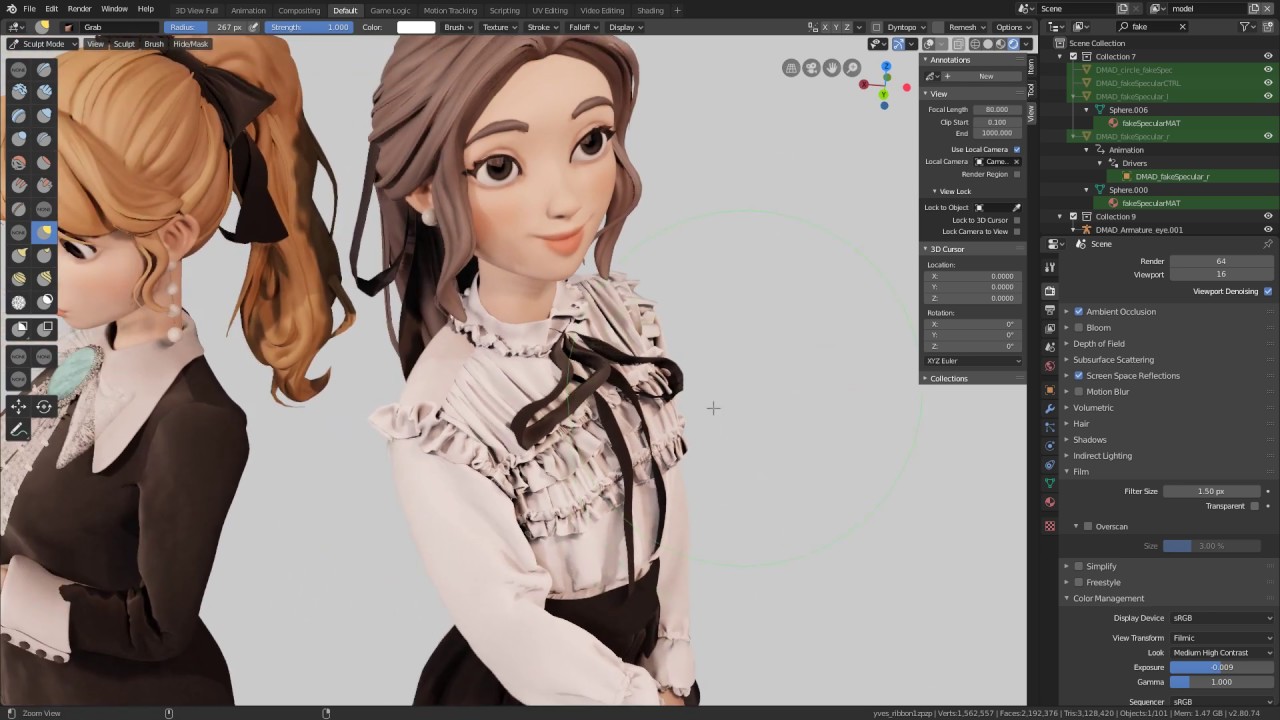
VI. Texture Painting and Detailing
A. Applying Textures and Color Detailing in Sculpted Models
Following the sculpting process, artists can enrich their models by applying textures and painting colors directly onto the surface of the sculpted models. This step enhances the visual appeal and realism of the sculpted model, adding depth and complexity to the overall design.
B. Adding Fine Details and Surface Texture
Incorporating surface details, such as skin pores, wrinkles, or subtle textural elements, contributes to the authenticity and visual richness of a sculpted model. By utilizing various brushes and advanced techniques, artists can add intricate, lifelike details to their creations.
VII. Retopology and Sculpting Optimization
A. Understanding Retopology for Clean Mesh Topology
Retopology involves reconstructing the topology of a sculpted model with an emphasis on creating clean and optimized geometry. This process is essential for ensuring that the sculpted model is animation-ready, lightweight, and suitable for efficient rendering.
B. Sculpting for Animation and Practical Considerations
Optimizing a sculpted model for animation and rigging involves ensuring that the model’s topology aligns with the requirements of deformation and motion. This practical consideration ensures that the sculpted models perform seamlessly in animation workflows.
VIII. Advanced Sculpting Techniques and Specialized Projects
A. Exploring Advanced Sculpting Workflows
Exploring advanced sculpting techniques, such as multi-resolution sculpting and displacement maps, provides artists with the means to create intricate and detailed models. These techniques further enrich the sculpting process, allowing for the creation of complex and high-fidelity models.
B. Specialized Sculpting Projects and Creative Applications
The versatility of sculpting extends to specialized projects, such as creature design, environmental assets, and fantasy art. Embracing creative applications and specialized projects challenges artists to push the boundaries of sculpting, fostering innovation and creativity.
IX. Practical Tips and Resources for Sculpting Mastery
A. Leveraging Online Resources and Community for Learning
Online tutorials, forums, and digital communities serve as invaluable resources for continuous learning and skill development in sculpting. Engaging with the wider Blender community fosters collaboration, enabling artists to seek feedback, share knowledge, and stay inspired.
B. Practical Tips and Best Practices for Sculpting in Blender
Adopting effective sculpting habits, implementing time management strategies, and organizing projects efficiently are pivotal to mastering sculpting in Blender. Practical suggestions and best practices facilitate creativity, skill development, and sculpting mastery, empowering artists to unleash their full artistic potential.

In conclusion, mastering sculpting in Blender is an immersive journey that opens a world of creative possibilities. From understanding the basics to exploring advanced techniques, sculpting in Blender empowers artists to breathe life into their designs, whether creating organic forms, character sculpting, or specialized projects. By leveraging practical tips and community resources, artists can continue to refine their skills, turning their artistic visions into stunning, three-dimensional realities. With its diverse applications in animation, gaming, and design, mastering sculpting in Blender is not only a means of artistic expression but also a fundamental skill for aspiring 3D artists and designers.